Electronic Music Interfaces Today
- Nov 26, 2025
- 7 min read
When electronic music first emerged more than a century ago, few musicians could have imagined a future where sound would be shaped by a machine as intricate as the computer. The computer today can be used to record, compose, mix, master and distribute music to the entire world.
Earlier if the composer imagined an orchestra, they would have to write the piece in the form of notation, work with a conductor and instrumentalists to bring their vision to life. They would also need access to mics, concert hall/recording studio to record the album along with a recording engineer present. Once it is recorded it needs to be mixed & mastered, pressed on a vinyl record by the record label and distributed physically to record stores. Only after around 2 months of pressing process, consumers would buy an LP for some amount of money but today a lot of music is available for free on streaming platforms.
In contrast, a modern day ‘Music Producer’ can alone do all the steps from composing to distributing. This shows how accessible music creation and consumption has become. Due to vast amounts of tools available today, figuring out the source of the sound is getting more difficult in recorded music. For example, if someone heard a piece by John Chowing in the 1980s with an amazing FM synth bass line, one could tell that it is the DX7. As a composer, if you wanted to play that sound in your composition you would have had to buy the synthesiser. Today, the same sound can be recreated using softwares like Max/MSP, Pure Data, Ableton, ProTools, etc.. We can also sample the sound from the Chowning’s piece and spread it across the keyboard. Therefore, knowing how the sound was created is more difficult than ever.
On the Internet we can download terabytes of sound packs and samples, Audio effects and Synthesizers. They can be manipulated in an infinite number of ways to make an infinite number of unique sounding compositions.
Now if anybody can make anything using a computer, why don’t they? The interface always has something that it can do easily and is good at. For example, a guitar can easily play chord progressions, tb-303 bassline synth can easily play bass sequences. If you try to play chords on the 303 bassline and use guitar as a sequencer it cannot be achieved easily. Interaction with instrument ,is crucial in what the resulting piece will be.
The interaction with the computer is primarily through the QWERTY keyboard and the mouse. The interaction with it is the same as that for viewing emails, buying stocks in the market and e-commerce. Miller Puckette known for creating the real-time audio/visual programming environments Max and Pure Data (Pd) calls computer music a “Desk Job”.
Another major shift in the last century has been in the way that music is consumed. On the phone there are so many audio files that can be accessed with just a few clicks. The concept of recorded music is very recent in the history of sound and it is more accessible now than ever. In the 1960s, the consumer had access to the Vinyl Records available at the local record store. Back then the listener was carefully choosing which record they wanted to listen to among the limited LPs that they had access to because music was expensive and less accessible. Today, the streaming platform’s algorithm, playlists and suggestions govern which music is more consumed and gets more popular. Streaming platforms want the consumer to stay on the platform as long as possible because it maximizes profits.
Also, music has become secondary to chores like driving, running, cooking but it is rarely not just about listening to music. This has to do with accessibility, rise in entertainment options like video and interactive mediums, accessibility of listening to music, reduced attention spans among many other reasons.
Electronic Music Instruments in 2025
Digital Audio Workstations(DAWs)
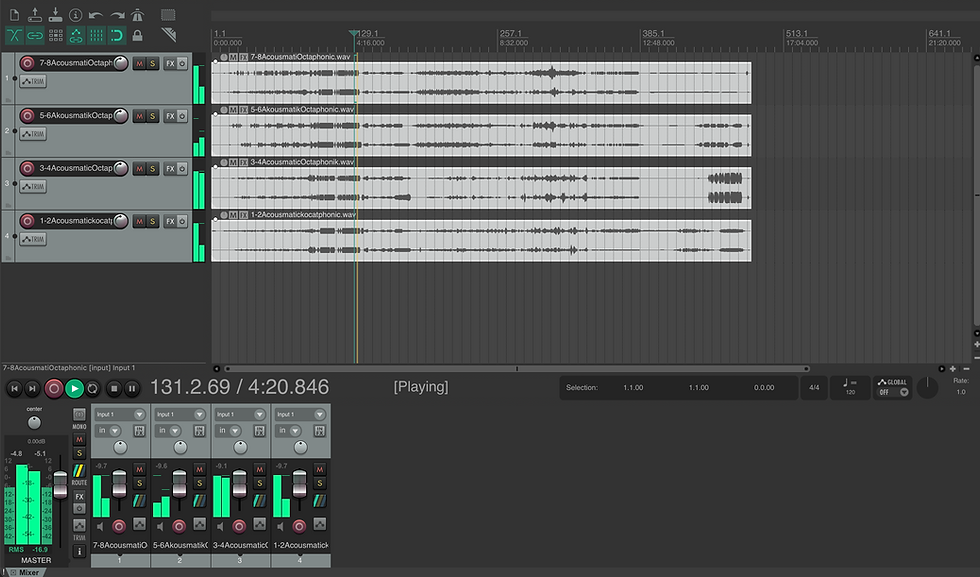
In essence, Digital Audio Workstations (DAW) turned computers into full-fledged recording studios. These are softwares that can generate and manipulate digital signals. It can also take in analog signals using a sound card that converts analog signals to digital. Majority music today is run through a DAW before it is distributed. Unlike traditional analog studios with bulky equipment and irreversible tape editing, DAWs allow non-destructive, precise manipulation of audio and MIDI data. This dramatically lowered the barriers to music production, making it accessible to a global audience beyond professional studios. This really democratized the tools available to the composers because everybody can buy, build similar tools to make music. This is to the degree that somebody in their bedroom uses the same Equalizer as the one used in Abbey Road Studios.
MIDI

Musical Instrument Digital Interface is the most widely used protocol today in electronic music. The reason for its popularity is its compatibility with modern DAWs, standardisation in hardware and cross talk between various interfaces. MIDI along with software is generally cheaper in comparison to hardware equipment including FX, synthesizers and mixers. The limitation with MIDI is that it is a western standardised concept. For example, one cannot play Ragas or Just Intonation because it follows 12 tone equal temperament. Also, it has 7-bit resolution for control change values (127 steps), which results in steps instead of smooth changes in musical expression in terms of pitch. MIDI channels control entire instruments, not individual notes, making it difficult to convey per-note expressive nuances like vibrato on individual strings.
Synthesizers

Synthesizers are electronic instruments that use analog or digital processing to generate sound.(https://www.soundgym.co/blog/item?id=what-is-a-synthesizer).
In the software realm one can make any possible sound using synthesizers of various kinds. On the other hand, every hardware synthesizer has a particular character. While using a software synthesizer the user is still using the computer and interacting with a QWERTY keyboard. On the other hand, hardware synthesizers can feel more intuitive and hands on.
The interaction with an analog synthesizer is hands-on as we have to plug-in and out wires, twist knobs and/or hit keys in order to generate sound. There are synthesizers where you can save patches and in some you can’t save the patch. In most cases, hardware synthesizers are more expensive than software synthesizers. Hardware synthesizers are bulky and not as easy to carry around as the software. They are limited to the sound engine and built-in modifiers. Unless, you choose to open them up.
In order to get a software synthesizer one has to download from the internet which in most cases is easier than buying a new synthesizer because of accessibility and pricing. So, one can download 1000s of synthesizers from the internet in merely a day. Let’s say there are 100 software synthesizers and they have 200 presets each. Now we have 20,000 sounds to choose from. This can be a little overwhelming and lead to noise because it can be very difficult to go through all the presets to find a sound. So, as a user one ends up only visiting the personal favourites as go to sounds. This vast pool of resources can lead to a lot of noise and not understanding the tool at a greater depth. Considering this, it is good to have limitations and to know the limited tools that we have at their disposal.
Having said that, software synthesizers are cheaper, very powerful sound design tools. With softwares like VCV Rack( Virtual Modular Synthesiser ) if the user wants to add one more module to the patch.. The user can drag and drop one. If they want to do the same in hardware, they have to spend a lot of money. Wait for it to get delivered or go to the nearby shop. Unbox the module and then mount it on my rack.
It is not that hardware is better than software or the other way around. They both have pros and cons. Chosing one or the other is also a creative choice.
Modular Synthesizers

There has been an increase in the use of modular synthesizers. These synthesizers have individual modules which talk to each other using Control Voltage protocol. Each module generates, inputs, manipulates and outputs sound. One module is routed to the other using patch cords.
From an interaction standpoint, it is particularly interesting because the “patch” on the modular synthesizer cannot be saved like in computers. It is tedious to recreate or remember a patch on a modular synthesizer because of so much wiring and potentiometer positions. This forces the composer to make decisions in real time i.e. either it works or it doesn’t. If the patch is recorded in the moment then it stays, otherwise it does not. In contrast to the Digital Audio Workstation where the user can later remove a track, edit or change it completely.
Creative Coding Environments

Creative programming environments like Max MSP, p5.js, Processing and many others are extremely powerful signal processing tools. These can come in very handy in running your own algorithms for manipulating pitch, randomness, AM, FM, granular synthesis, probability based triggers to name a few examples. It can be used to compose for spatial audio systems as some softwares and plug-ins like Ableton can work only with 2 channels of audio. These can be very useful to design interactive interfaces as they are flexible when it comes to understanding protocols and connect to most micro-controllers. While these programmes come with objects or UGens from before for ease of use. You can make your own objects , devices or even environments to work in as per your liking.
Conclusion
Music is fundamental in society, culture, languages and religions. People are very emotionally attached to musical instruments and musicians. Today, the tools at our disposal are very vast and accessible. Anybody can write a few sentences of text and get a song generated using AI. Does this make them a musician? We can also jam with AI-augmented instruments. Does it make the music inhuman? Billboard no.1 songs are AI generated today. Does it make the music fake? This is truly an alarming and exciting time for tools in electronic music. One can conclude that the barrier for music making, performing, collaborating and listening to music has lowered drastically.



Comments